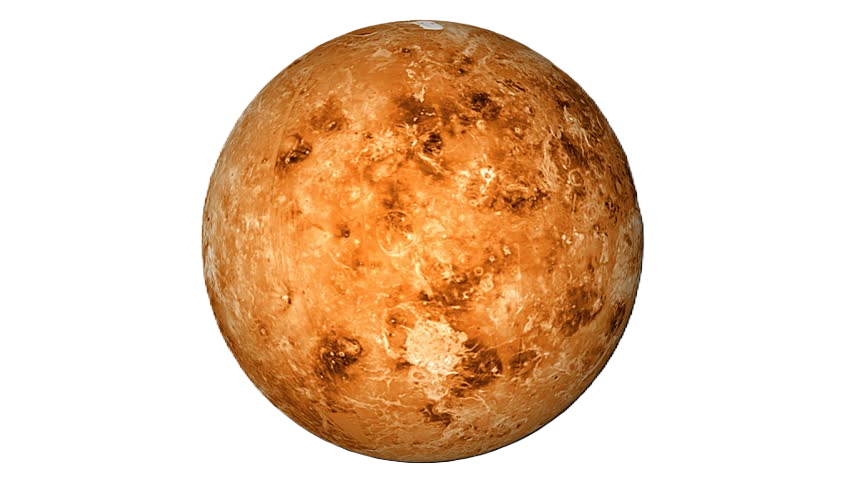

Venus, often called Earth’s twin, is similar in size and structure to our planet but vastly different in other ways. It’s the hottest planet in the Solar System, with surface temperatures exceeding 470°C, hot enough to melt lead. This extreme heat is due to a runaway greenhouse effect caused by its thick atmosphere of carbon dioxide.
The planet’s surface is covered with vast plains, volcanic mountains, and craters. Venus rotates backward (retrograde rotation) compared to most planets, so the Sun rises in the west and sets in the east.
Venus formed from a similar process to Earth but experienced a divergent evolution due to its closer proximity to the Sun. Its thick atmosphere traps heat, leading to its runaway greenhouse effect. Venus has:
Venus’s atmosphere provides a natural laboratory for understanding climate change and atmospheric science.